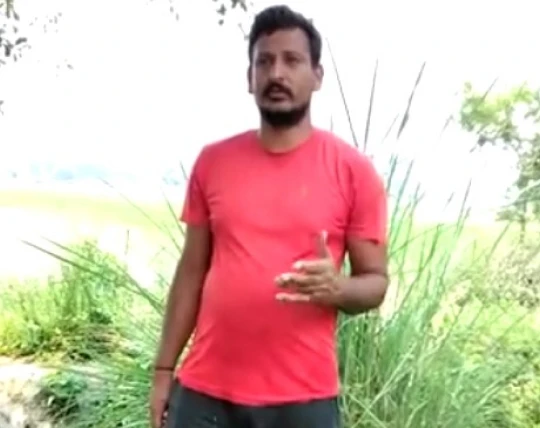
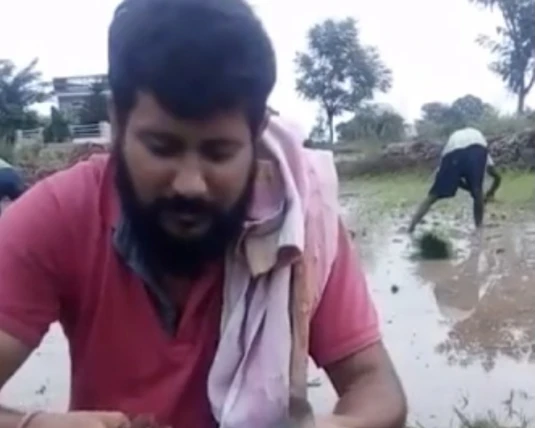
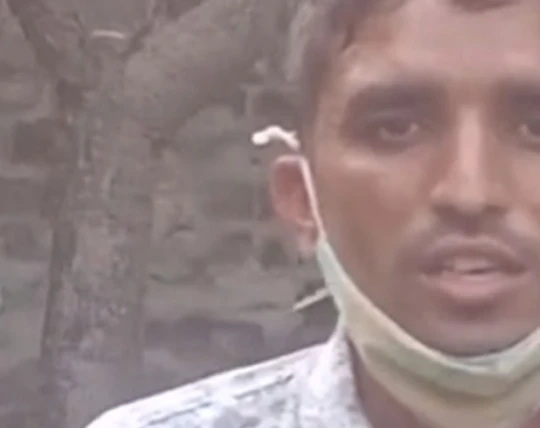
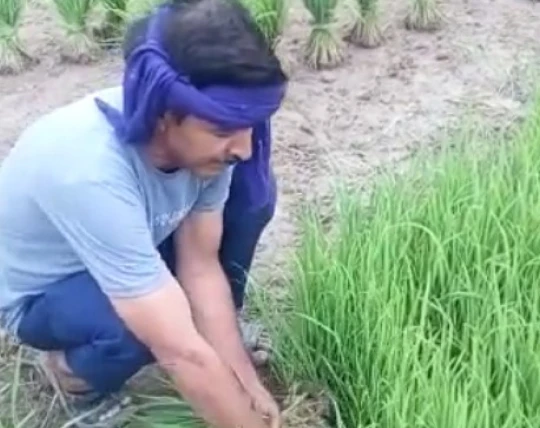
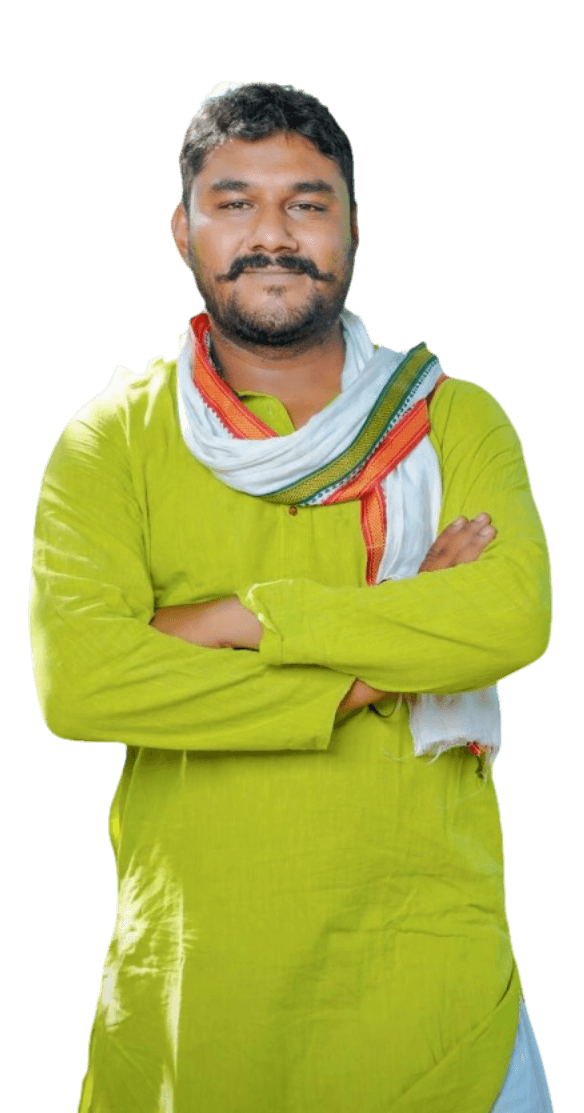
Our farmers from Laksar cultivate a variety of organic and sustainably grown crops like Basmati, Wheat, Rajma, and more, which are then fine-graded and checked for quality assurance before distribution.


NBF’s Laksar Project is situated in Laksar, district Haridwar, Uttarakhand, India. The Haridwar district is located in the southwestern part of Uttarakhand State. The Indo-Gangetic belt in this district has three-tier aquifer systems, separated by thick confining clay layers of varying thickness. From the geomorphological prespective Haridwar can be divided into 4 seprate units and they are flood plains, upper piedmont plains, structured hills and lower piedmont plains. The alluvial sediment’s complexity is ideal for crop cultivation, including wheat, mustard, oats, and peas. Haridwar, known as the gateway to God Hari, is a spiritual and religious hub. The farmers in this project are cooperative and open to adopting new technologies, making them adaptable to change.
NBF’s Project Haridwar

Location of the Project
The Laksar Project is located in Haridwar district, Uttarakhand, India, which is one of the six blocks of Haridwar. Haridwar is considered one of the seven sacred cities for Hindus, making it a significant pilgrimage center. The Sanskrit translation of Haridwar is “the door of Gods,” emphasizing its religious and spiritual significance.
The geographical coordinates for the Laksar Project are 29.945°N 78.163°E, providing precise information about its location.
Organic Certification
NPOP Certified Haridwar Project

Nature Bio Foods’ (NBF) Lakshar Haridwar project is certified by the National Program for Organic Production (NPOP) as it follows the guidelines and standards set by NPOP. NBF implements various organic farming practices, including crop rotation, use of organic manure, and natural pest control methods, to ensure the production of organic crops.
The Lakshar Haridwar project also uses modern technologies and techniques to enhance the efficiency and productivity of organic farming. NBF works closely with the farmers in the project to provide them with training and education on organic farming practices, enabling them to adapt to new technologies and methods.
To ensure compliance with NPOP standards, NBF undergoes regular inspections and certifications by accredited third-party certification bodies. NBF also maintains accurate documentation of its organic farming practices and processes to ensure transparency and traceability throughout the production chain.
Everything you need to know about Laksar, Haridwar
Laksar is a city in Haridwar located on the right bank of the Ganga River, at the foothills of the Shivalik ranges. The topography of Haridwar is undulating in the northern region and smoother towards the south, with a total altitude ranging from 868 m to 233 m. In the area near the popular Siwalik hills of North India, the gradient is steep. Geomorphologically, Haridwar can be divided into four distinct units: flood plains, upper piedmont plains, structured hills, and lower piedmont plains.
Agricultural Characteristics
Soil Profile

The Haridwar district falls under the hot sub-humid (dry) eco-region and has alluvium-derived soils. The climate of this eco-region is hot and sub-humid (dry), covering the northern Indo-Gangetic Plain, including the Piedmont Plain of the Western Himalayas. The soil in all five blocks of the Haridwar district is fertile, particularly near the Solani river. While the clay percentage is higher in some places, the soil is suitable for all kinds of crops. Our team has regularly interacted with farmers to increase soil fertility, which was evidenced by the production of PB-1637 last year.

Alluvial Soil – This soil is derived from the alluvial deposits of the Ganges river and is rich in organic matter, making it highly fertile.

Red Soil – This soil is formed from weathered crystalline rocks and is characterized by its reddish color. It is rich in iron and aluminum oxides but has low fertility.

Loamy Soil – This soil is a mixture of sand, silt, and clay and is highly suitable for agriculture due to its high fertility and water retention capacity. It is found in various parts of Haridwar district.
Climate Condition
Haridwar enjoys a pleasant climate for most of the year, owing to its location at the foothills of the Himalayas. The climate remains moderate throughout the year, with temperatures rarely reaching extreme levels, although the city experiences heavy rainfall. The average annual rainfall in Haridwar is about 2136.7 mm. During the summer months, the temperature ranges from 35°C to 45°C, making it mild and moderate. The monsoon season follows the summer season, bringing good rainfall. In the winter months, the temperature ranges from 10°C to 30°C, and the weather can be unpredictable, with very cold temperatures that require warm clothing.
Temp.
Minimum

10 °C
(Dec-Jan)
Maximum

45 °C
(May-June)
Humidity
Relative Humidity

70 %
Rainfall
Average Rainfall

2136.7 mm
Seasons
There are mainly three seasons.

Summer
(Mar-June)

Rainy
(July-Sep)

Winter
(Oct-Feb)
Farm Water Availability
In Haridwar district, both surface and subsurface sources of water are utilized for irrigation purposes. Farmers, as well as government agencies, have constructed canals and guls from perennial rivers, springs, seasonal rivulets, and gadheras. The canals in the district run for a length of 9,575 km and are a major source of surface water for irrigation, along with rivers, streams, irrigation ditches, and impounded water such as ponds, reservoirs, and lakes. Groundwater from wells is also a significant source of water for agriculture in Haridwar. Additionally, locally collected rainwater in cisterns and rain barrels is utilized to enhance crop production.
Nature of Farmers
Farmers in the Haridwar region are known for their hardworking and cooperative nature, and they often help each other when needed. In the past, farmers did not hire labor for agricultural work because they lived in joint families with many members who could perform the work. However, in modern times, with the decline in joint families, most farmers hire labor for agricultural work. Farmers are also interested in learning new techniques and are inclined towards organic farming. They are open to adopting new techniques, such as the System of Rice Intensification (SRI), homemade inputs like composts, bio-pesticides, and liquid manures, to improve their crop production.
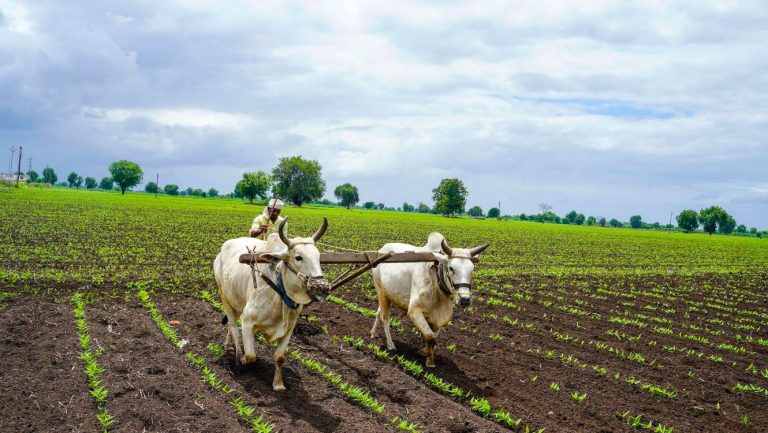


Growing Conditions
The agro-climatic conditions in Haridwar are suitable for the cultivation of most Kharif and Rabi crops. The region experiences a humid and sub-humid climate, with three distinct crop seasons. The annual rainfall in Haridwar is predominantly received during the Kharif season (84%), while the Rabi and Zaid seasons receive only 16% of the rainfall. The topography of the district is variable, with the Shiwalik range (869 m) located in the north and plain land (232 m) present in the south.
Crop Details
Laksar in Haridwar is known for its diverse agriculture and cultivation of various crops. The fertile soil, favorable agro-climatic conditions, and availability of both surface and groundwater make Laksar an ideal place for agriculture.
Kharif
- Basmati Paddy CSR-30
- Sarbati.
- PB1637
- Type-3
- Kasturi
- PB-1
- Pusa 1121
- Sugarcane

Rabi
- Wheat
- Mustard
- Oats
- Peas

Statistics
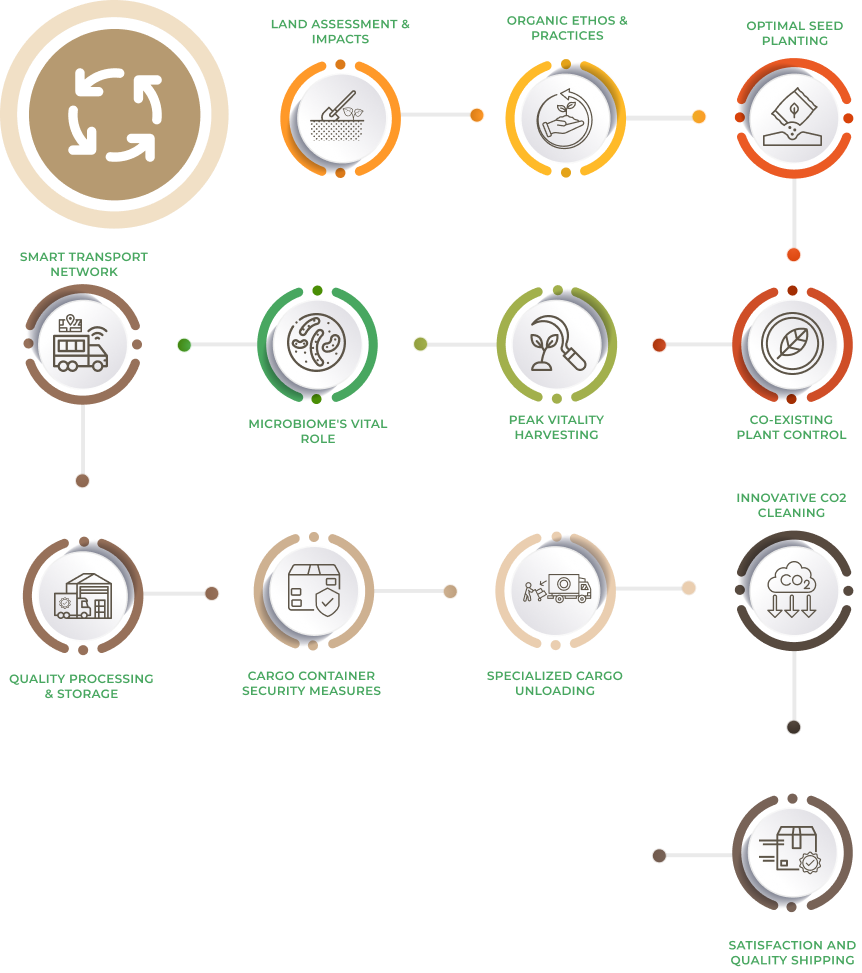
NBF Supply Chain
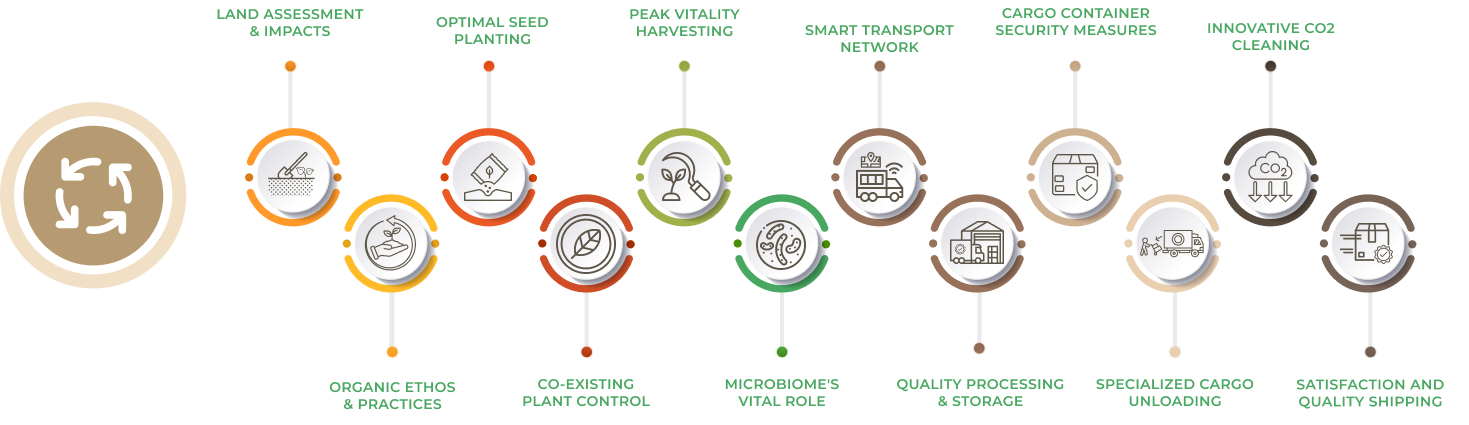
NBF Supply Chain
How to Reach Laksar, Haridwar?
Laksar, Haridwar is well connected depicted being on semi-mountainous terrain. There are various modes of transportation to reach Laksar and Haridwar, including:

By Train
Laksar has a railway station, which is well-connected to major cities in India, including Delhi, Mumbai, Kolkata, and Chennai. Haridwar also has a railway station that is connected to major cities in India. Trains are an affordable and convenient mode of transportation to reach these destinations.

By Road
Laksar, Haridwar are well-connected by roads and highways, and there are many buses, taxis, and private cars available for hire. You can also take a bus from Delhi, Dehradun, or other nearby cities to reach Haridwar. Laksar, Haridwar is well-connected by highways and roads, and there are ample parking spaces available.
By Air
The nearest airport to Laksar, Haridwar is the Jolly Grant Airport in Dehradun, which is about 40 kilometers away. From the airport, you can hire a taxi or take a bus to reach Laksar.

Places to Visit in Laksar, Haridwar
Crystal World
Crystal World is a popular water park located in Laksar, Haridwar. It is an ideal place to visit with family and friends, especially during the summer months. The park offers a variety of water rides, slides, and attractions, along with restaurants and snack bars. It is a perfect spot to beat the heat and have some fun.
[/mvc_ihe]Piran Kaliyar Sharif
Piran Kaliyar Sharif is a famous Sufi shrine located in Laksar, Haridwar. It is believed to be the tomb of the 13th-century Sufi saint, Hazrat Alauddin Ali Ahmed Sabir Kalyari. The shrine is visited by thousands of devotees every year, and it is a symbol of religious harmony as people from all religions come here to seek blessings. The shrine also has a mosque and a dargah, and it is an important pilgrimage site in Haridwar district.
[/mvc_ihe]

Elevation
Haridwar has an average elevation of approximately 287 meters above sea level.


River
The town is situated on the west bank of the Ganges floodplains.


Soil
The most common soil type in Laksar, Haridwar is Alluvial soil. Apart from alluvial soil, the region also has other soil types, such as sandy soil, loamy soil, and clayey soil.


Crop
Some of the major crops grown in the region include Wheat, paddy, Mustard, Oats and Pea.
Sustainability Efforts
Economic
| Women's Empowerment through Entrepreneurial Training Programs |
675 |
|
| Empowering Young Women: Career Counseling for Future Success |
234 |
|
| Craftsmanship Unleashed: Skill Development in Artisanal Handicrafts |
456 |
|
Social
| Nourishing the Future: Workshop on Child Nutrition and Well-being |
550 |
|
| Guiding the Leaders of Tomorrow: Mentoring Programs for Students |
950 |
|
Environmental
| Cultivating the Earth: Advanced Training in Soil Regeneration |
464 |
|
| Towards a Plastic-Free Future: Comprehensive Reduce and Reuse Initiatives |
123 |
|
| Preserving Our Lifeline: Campaigns for Water Conservation and Stewardship |
232 |
|
| Agriculture in Harmony with Nature: Organic Farming workshops |
987 |
|
| Clean Village, Healthy Village: Promoting Cleanliness and Sanitation at the Grassroots Level |
987 |
|