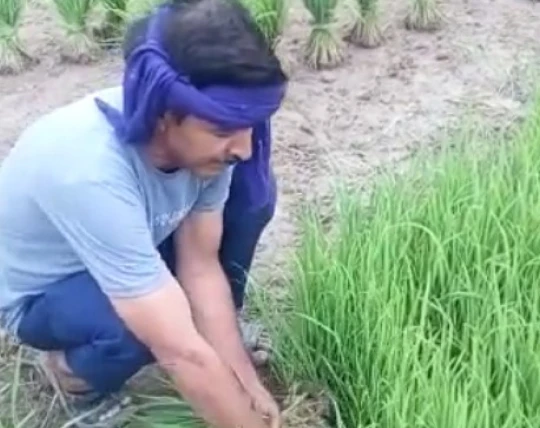
Our farmers from Mithila cultivate a variety of organic and sustainably grown crops like Wheat, Maize, Mustard, Lentil,Flaxseed and more, which are then fine-graded and checked for quality assurance before distribution.


Let us tell you about the Mithila project of Nature Bio Foods. Geographically, NBF Mithila project is located in Darbhanga, which is bounded north by the Madhubani district, south by the Samastipur district, east by the Saharsa district, and west by Sitamarhi and Muzaffarpur districts. Darbhanga district is devoid of any hills and thus it has a vast alluvial plain. This district has a gentle slope from north to south.
NBF’s Project Mithila

Location of the Project
Located in the heart of Mithilanchal, the fertile alluvial plains of North India, Darbhanga is an important district in North Bihar. Darbhanga is a district located in the state of Bihar in eastern India. It is situated in the northern region of Bihar and is part of the ancient region of Mithila, which is spread across the northern part of Bihar and southern part of Nepal.
Coordinates – Geographical Coordinates for the Mithila Project are 26.190831429951913, 85.89432792222398.
Organic Certification
NPOP Certified Mithila Project

Nature Bio Foods Mithila project is certified organic by the National Program for Organic Production (NPOP), which is the regulatory body responsible for implementing organic certification in India.
To obtain NPOP certification, the Mithila project underwent a rigorous certification process that involved a thorough inspection and evaluation of the entire organic farming system, from the farm to the processing and distribution facilities.
The NPOP certification program is designed to ensure that organic produce is grown and processed using strict organic standards that prohibit the use of synthetic pesticides, fertilizers, and genetically modified organisms (GMOs). It also ensures that the farmers and processors adhere to strict guidelines for sustainability, environmental protection, and social responsibility.
The NPOP certification of the Mithila project is a testament to Nature Bio Foods’ commitment to promoting sustainable and ethical agriculture practices in India. It provides assurance to customers that the organic produce sourced from the Mithila project is of the highest quality and meets the stringent standards set by the NPOP.
Everything you need to know about Mithila, Bihar
Located in the Darbhanga region, NBF Project Mithila is divided into four natural regions. The first division lies in the east and comprises three blocks: Ghanshyampur, Kusheshwarasthan, and Biraul. These blocks contain fresh silt deposited by the Kosi River, which once flooded the area before the Kosi embankment was constructed during the second Five-Year-Plan. This region is mostly covered with wild marsh and sandy lands.
The second division lies south of the Boorhi Gandak River and is the most fertile area in Darbhanga. It sits at a higher elevation than the rest of the district, and its few marshes make it ideal for growing rabbi crops on a large scale.
The third division is the low-lying doab areas between the Boorhi Gandak and Bagmati rivers. These areas get flooded every year, creating chaur and marshes.
The fourth division is the Sadar subdivision, which includes several streams and some up-lands.
Agricultural Characteristics
Soil Profile

The soil in project Mithila is a mixture of alluvial, sandy loam, and calcareous clay and sand in varying proportions. Its fertility status ranges from low to medium. During the rainy season, low-lying areas are prone to water inundation, which dictates the selection of paddy cultivars. A significant portion of the low-lying chaur land remains flooded throughout the year.

Alluvial soil is found in abundance as it is formed from the deposits of the rivers that flow through the region.

Clay soil is found in many parts of the Mithila region and is known for its heavy and sticky texture.

Sandy soil is also prevalent because of the region’s proximity to rivers and the prevalence of sand in the area.
Climate Condition
The district enjoys a dry and healthy climate with three well-defined seasons: winter, summer, and rainy season. The cold weather sets in from November and lasts until February, with March also being relatively cool. In the second half of March, westerly winds start to blow, and the temperature rises considerably. May is the hottest month, with temperatures reaching up to 107 degrees Fahrenheit. Rainfall begins in mid-June, and with it, the temperature drops and humidity rises. The moist heat during the rainy season can be oppressive until August, with rainfall continuing until mid-October. On average, the district receives 1142.3 mm of rainfall, with around 92% of the total rainfall occurring during the monsoon period.
Temp.
Minimum

2.7 °C
(Dec-Jan)
Maximum

46.8 °C
(May-June)
Humidity
Relative Humidity

66.1 %
Rainfall
Average Rainfall

1142.3 mm
Seasons
There are mainly three seasons.

Summer
(Mar-June)

Rainy
(July-Sep)

Winter
(Oct-Feb)
Farm Water Availability
In project Mithila, the primary source of irrigation is still rainfall, as only 19% of the total cultivable area has access to other sources of irrigation. Historically, irrigation in the district has been linked to flood control measures and drainage schemes. However, in recent years, there has been a considerable effort to expand irrigation facilities by tapping into ground water resources and implementing lift irrigation schemes under the minor irrigation system. Currently, around 70% of the total irrigated area in the district is being irrigated from ground water sources.
Nature of Farmers
The nature of farmers in the Mithila region is largely shaped by their traditional values and strong attachment to the land. Agriculture has been the mainstay of the economy in the region for generations, and farmers take great pride in their work. They have a deep knowledge of the local soil and weather conditions and use traditional farming methods passed down through the generations. Despite facing numerous challenges such as erratic weather patterns, land degradation, and a lack of modern farming technologies, farmers in the region are known for their resilience and resourcefulness. They are hardworking and dedicated to their craft, and their commitment to sustainable agriculture practices ensures that the land is used in a responsible and productive manner.
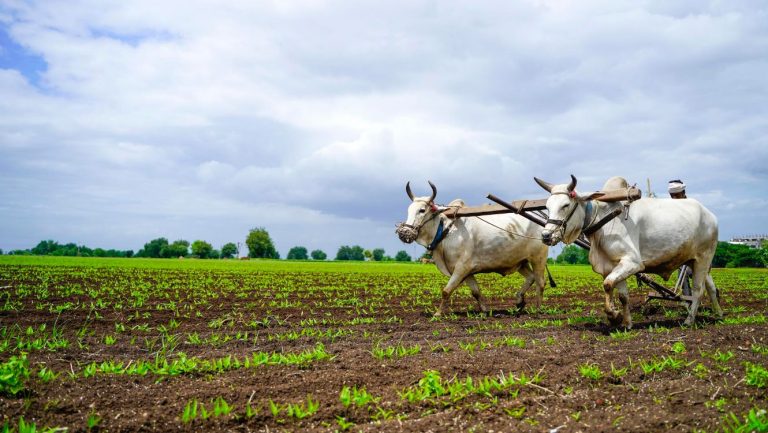


Growing Conditions
In Mithila, the vast majority of households – around 95 percent – do not own or control the means of production. Of these, 67 percent are landless and 28.12 percent are marginal farmers. Only a small proportion of the population are small (3.19 percent), medium (1.04 percent), or large (0.87 percent) farmers. Marginal farmers typically have an average land size of 0.88 acres, while small, medium, and large farmers have land sizes of 3.77 acres, 7.51 acres, and 28.07 acres, respectively.
Due to the small landholdings, most farmers rely on on-farm inputs for soil nutrient management, and manual labor is used for weeding, harvesting, and post-harvest practices.
Crop Details
The cultivable area in Darbhanga district covers 82.17% of the total land. Paddy is the most widely grown Kharif crop, occupying 96% of the sown area, with maize and oil seeds following at 2.1% and 1.5%, respectively. During the Rabi season, wheat is the principal crop, covering around 54% of the sown area. Other crops include pulses (21%), maize (10%), oil seeds (9.4%), and potato (6%).
Kharif
Paddy, Maize

Rabi
Wheat, Maize, Mustard, Lentil, Flaxseed

Statistics
NBF Supply Chain
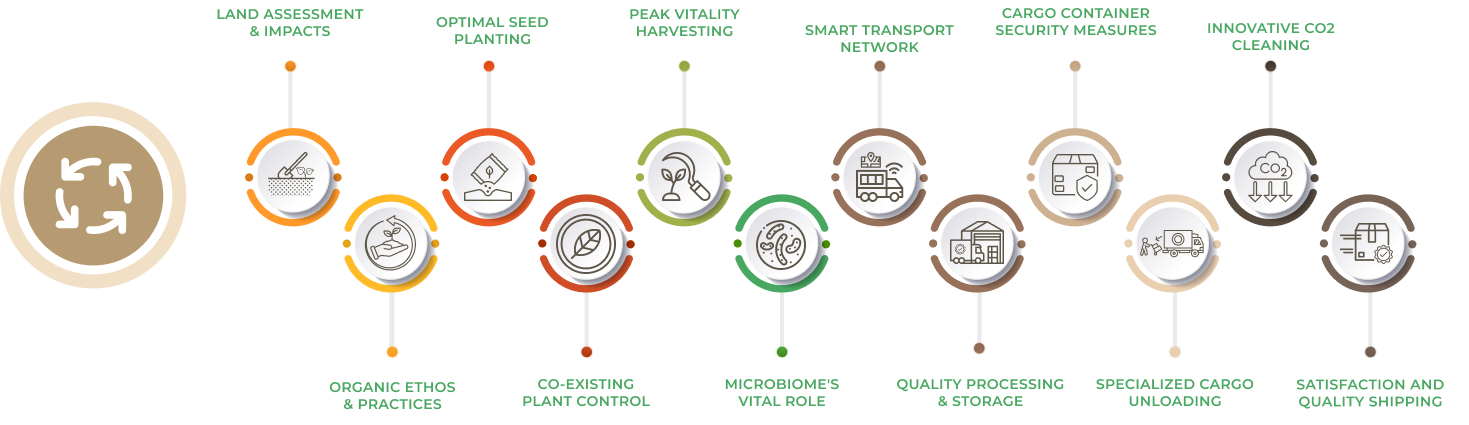
NBF Supply Chain
How to Reach Mithila?
Mithila is easily accessible from all over India through road, rail, and air transport depending on the location of interest. It is well-connected by highways and major roads to nearby cities and towns. Rail transport is also available with important railway stations in and around Mithila. For those coming from distant places, several airports in nearby cities offer flights to Mithila.

By Train
The major railway stations in Mithila are Darbhanga Junction, Samastipur Junction, and Jaynagar Junction. These stations are well-connected to major cities like Delhi, Kolkata, and Mumbai through regular trains.

By Road
Mithila can be reached via national and state highways. There are several bus services available from nearby cities like Patna, Darbhanga, and Madhubani to various towns and villages in Mithila.
By Air
The nearest airport to Mithila is Darbhanga Airport, which is located in the Darbhanga district. However, currently, there are limited flights operating from this airport. The other airports that are located near Mithila are Patna Airport and Gaya Airport. Both these airports are well-connected to major cities in India and have regular flights to and from various destinations.

Places to Visit in Mithila, Bihar
Shyama Kali Temple
The beautiful Shyama Kali Temple in Darbhanga, Bihar is the perfect place to visit for the spiritual tourists. Built in the year 1933, also known as Shyama Mai, this place hosts the annual Shyama Mai festival which is a popular fiesta.
[/mvc_ihe]Chandradhari Museum
Chandradhari Museum established by the state government in 1957, is situated at Darbhanga in Bihar, Originally situated on the eastern bank of Mansarowar Lake, The museum was shifted to the present double-storied building in 1974. The Museum with the help of the private collection of Chandradhari Singh, a zamindar of Madhubani Chandrandar Museum was established on 7 December 1957.
[/mvc_ihe]

Elevation
It has an average elevation of roughly 52 meters.


River
It lies to the east of the Bagmati river.


Soil
The soil of Darbhanga district is alluvial, sandy loam.


Crop
Horticulture crops include:
Kharif: Paddy, Maize,
Rabi: Wheat, Maize, Mustard, Lentil, Flaxseed
Sustainability Efforts
Economic
| Women's Empowerment through Entrepreneurial Training Programs |
671 |
|
| Empowering Young Women: Career Counseling for Future Success |
456 |
|
| Craftsmanship Unleashed: Skill Development in Artisanal Handicrafts |
123 |
|
Social
| Nourishing the Future: Workshop on Child Nutrition and Well-being |
600 |
|
| Guiding the Leaders of Tomorrow: Mentoring Programs for Students |
700 |
|
Environmental
| Cultivating the Earth: Advanced Training in Soil Regeneration |
456 |
|
| Towards a Plastic-Free Future: Comprehensive Reduce and Reuse Initiatives |
2342 |
|
| Preserving Our Lifeline: Campaigns for Water Conservation and Stewardship |
568 |
|
| Agriculture in Harmony with Nature: Organic Farming workshops |
764 |
|
| Clean Village, Healthy Village: Promoting Cleanliness and Sanitation at the Grassroots Level |
875 |
|
Our Impact
Impact of our Farmers
The impact of our farmers is significant in enhancing soil fertility through various methods such as crop rotation, cover cropping, reduced tillage, and application of compost. These practices reduce fuel-intensive tillage, resulting in carbon sequestration, decreasing greenhouse gases, and reversing climate change. In addition, they can improve soil structure and reduce the possibility of soil erosion.

Difference our People are Making
The difference our organization is making is by converting land from conventional management to organic management, managing the entire surrounding system for biodiversity and sustainability, and using alternative sources of nutrients such as crop rotation, residue management, and organic manures. We provide complete biological inputs to our crops, and our teams supervise and manage weed and pest control through better management practices, physical and cultural means.
Contribution by our Customers
Our customers’ contribution is vital in promoting food safety and environmental issues. The concern for their health, the environment, and worldwide crises has increased exponentially. Organic agriculture has become the only option for many consumers. Simply by consuming organic produce, they are contributing to the overall health of the planet and making an impact towards sustainability.