Our farmers from Pithapura cultivate a variety of organic and sustainably grown crops like Pearl millet, castor, groundnut, Barley, Wheat, Amaranth, Quinoa, Mustar and more, which are then fine-graded and checked for quality assurance before distribution.


This batch of crops is from the Organic Farms of Pithapura, a village located in the Reodar Tehsil of the Sirohi District, Rajasthan. Situated in the Jodhpur Division, Pithapura is 66 kilometers west of the district headquarters in Sirohi and 16 kilometers from Reodar. The state capital, Jaipur, lies 502 kilometers away. This region, known for its unique geography and agricultural practices, contributes significantly to the organic produce market.
The Pithapura project grows various Rabi, Kharif, and Zaid crops, such as like Pearl millet, castor, groundnut, Barley, Wheat, Amaranth among others. The project prioritizes organic farming practices, ensuring that all the NOP and COR laid standards of organic farming are being followed while developing healthy and fertile soil for long-term production.
Organic Farms of Pithapura, Rajasthan

Location of the Project
Pithapura project is situated in the Sirohi district on the border of Rajasthan and Gujarat. Located 210 km from Ahmedabad, 207 km from Udaipur, and 255 km from Jodhpur, it is surrounded by the districts of Jalore, Barmer, Abu Road, and Banaskantha. Pithapura, a village in Taluka Reodar, is 77 km from the district headquarters.
Coordinates – 24.604417°N 72.379486°E.
Organic Certification

Nature Bio Foods Pithapura project is certified organic by the National Organic Program (NOP), which is the regulatory body responsible for implementing organic certification in India.
To obtain NOP certification, the Pithapura project underwent a rigorous certification process that involved a thorough inspection and evaluation of the entire organic farming system, from the farm to the processing and distribution facilities.
The NOP certification program is designed to ensure that organic produce is grown and processed using strict organic standards that prohibit the use of synthetic pesticides, fertilizers, and genetically modified organisms (GMOs). It also ensures that the farmers and processors adhere to strict guidelines for sustainability, environmental protection, and social responsibility.
The NOP certification of the Pithapura Project is a testament to Nature Bio Foods’ commitment to promoting sustainable and ethical agriculture practices in India. It provides assurance to customers that the organic produce sourced from the Pithapura project is of the highest quality and meets the stringent standards set by the NOP.
Rooted in the Majestic Sands of Western India
The Pithapura Project of Nature Bio Foods involves 496 farmers working across 1,411.12 hectares of organic farming land. Located in the Sirohi District, Pithapura is characterized by its hilly and rocky terrain, divided by the granite massif of Mount Abu running from northeast to southwest. The southern and southeastern parts of the district, lying between Mount Abu and the main spine of the Aravallis, are rugged and mountainous, drained by the West Banas River. This region features dry deciduous forests, while the higher elevations of Mount Abu are covered in conifer forests.
Agricultural Characteristics
Soil Profile

The region predominantly features sandy soils with generally low water-holding capacity. Based on the soil profile, three types of strata are identified: deep soils covering 70% of the area, medium-deep soils accounting for 25%, and shallow soils making up the remaining 5%.

Sandy Loam to Clay Loam: The soil texture ranges from sandy loam to clay loam.
Color: Soil colors typically vary from grayish brown to yellow brown.
Catchment Area: The major area of these soils lies within the catchment area of the Banas River.
Climate Condition
Pithapura, nestled in the picturesque Sirohi district, experiences a semi-arid climate typical of the region. The summers are scorching, with temperatures often soaring above 100°F (37.8°C). May is the hottest month, while January brings cooler weather. Monsoons arrive in July, bringing an average annual rainfall of approximately 14.07 inches. Wind speeds remain moderate throughout the year. Overall, Pithapura’s climate reflects the arid beauty of Rajasthan, with distinct seasonal variations.
Temp.
Minimum

4°C
(Dec-Jan)
Maximum

49°C
(May-June)
Humidity
Relative Humidity

20-80%
Rainfall
Average Rainfall

622 mm
Seasons
There are mainly three seasons.

Summer
(Mar-June)

Rainy
(July-Sep)

Winter
(Oct-Feb)
Farm Water Availability
Only 5% of the project area relies on rain-fed agriculture, while irrigation facilities are available for the remaining 95%. The primary source of irrigation is tube wells, which account for 95% of the water supply for the covered area. Other potential sources like reservoirs, canals, and farm ponds currently contribute 0% to the water availability.
Most farmers in the region use sprinkler irrigation systems. This method is efficient and suitable for the local conditions. Additionally, the groundwater quality in the area is neutral, making it suitable for various agricultural practices.
Nature of Farmers
The demographics of farmers in the region present a diverse landscape. While a significant portion of senior citizen farmers grapple with illiteracy, mid-age farmers are generally literate and capable of reading and writing. Despite differences in education levels, there is a prevailing sentiment of respect towards individuals from outside the community. Moreover, farmers exhibit a deep-rooted attachment to their age-old traditions and customs, which play a significant role in shaping their agricultural practices. Despite this traditional outlook, there is a willingness among farmers to embrace new technologies, cooperating in the implementation of modern farming methods. Their eagerness to acquire new knowledge and inputs underscores a forward-looking approach towards improving farming techniques and yields.


Growing Conditions
In the region, traditional seeds are exclusively utilized by farmers, ensuring the maintenance of international quality standards by avoiding contamination from hybrid and GMO seeds. The agricultural landscape, largely desert with some irrigated areas, prompts farmers to employ sprinkler irrigation methods, fostering favorable conditions for the cultivation of cereals, oilseeds, and minor millets, resulting in optimal quality produce. Moreover, the high population of livestock in the area has deterred the widespread use of modern chemical fertilizers, paving the way for the continued advancement of traditional and organic farming practices.
Crop Details
Rice cultivation is an integral component of the rich cultural heritage of the state.
Crops: Traditional Basmati, Red Rajmash, Amaranth, Wheat & Mustard
Kharif
-
- Pearl millet
- Castor
- Goundnut

Rabi
- Wheat
- Amaranth
- Quinoa
- Mustard

Statistics
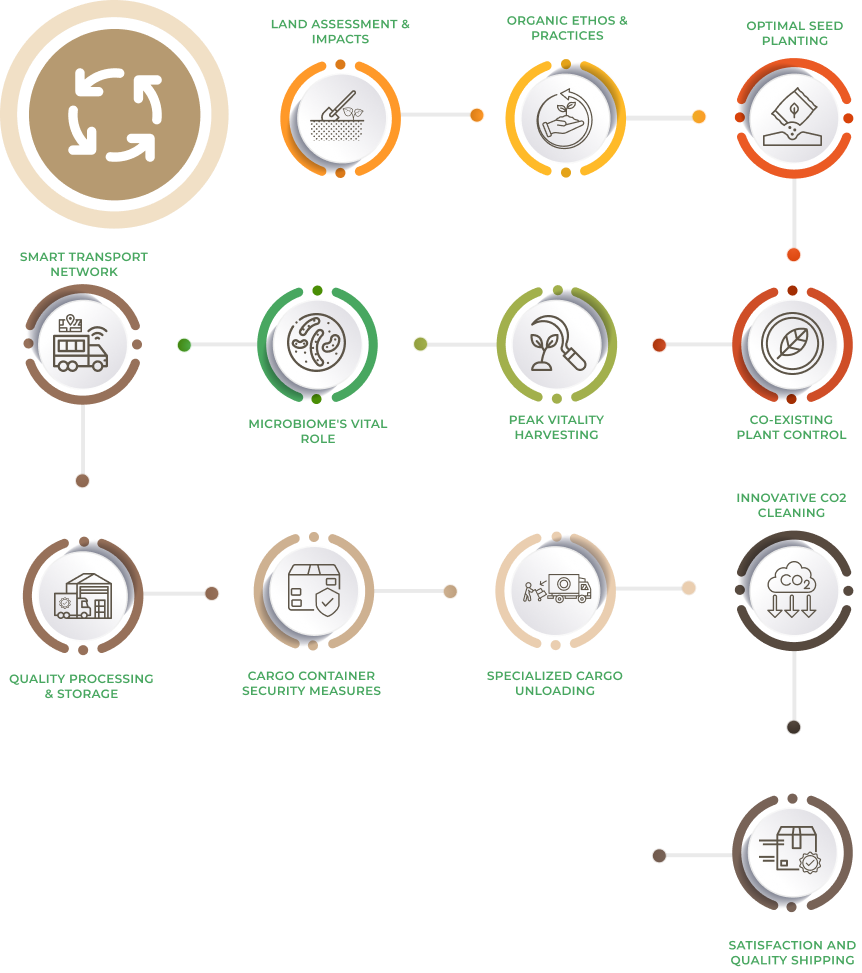
NBF Supply Chain
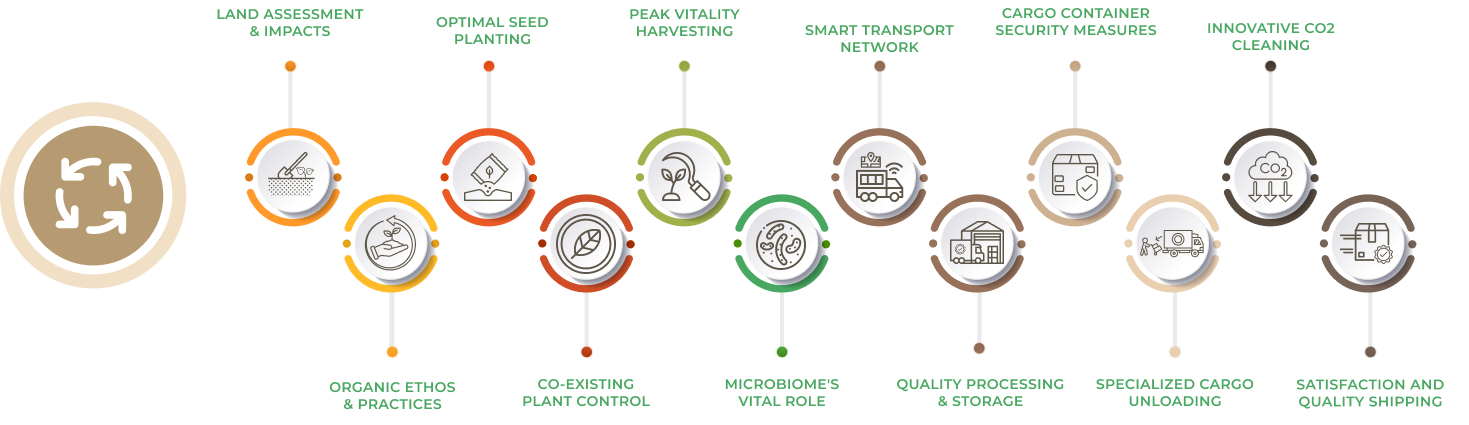
NBF Supply Chain
How to Reach Pithapura, Rajasthan?
Sirohi, a captivating district in Rajasthan, lies on the border with Gujarat. To get there, you have a few options:

By Train
Several trains connect Sirohi with other parts of Rajasthan and India. You can find train services from Sirohi town and Abu Road railway station.

By Road
If you prefer road travel, take National Highway 14, which links Sirohi to Gujarat and Pali. State Highway 19 connects Sirohi with Jalore district. Buses also run regularly between these places.
By Air
The nearest airport is in Udaipur, approximately 110 km away. Udaipur airport is well-connected to Jaipur and other cities by flights. Additionally, Sirohi itself has an airstrip.

Places to Visit in Pithapura, Rajasthan
MOUNT ABU
The only hill station in Rajasthan, Mount Abu is a welcome respite from the desert heat. Here, you can enjoy boating on Nakki Lake, visit the Dilwara Jain Temples, renowned for their intricate marble work, hike to the peak of Guru Shikhar, the highest point in Aravalli Range, and explore the Achalgarh Fort, a 14th-century citadel.
[/mvc_ihe]SIROHI
The headquarters of the Sirohi district, Sirohi is known for its beautiful stepwells and historic Sirohi Fort. You can also visit the Government Museum here to learn about the region’s history and culture.
[/mvc_ihe]

Elevation
It has an average elevation of roughly 270 meters.


River
West Banas River.


Soil
Two types of soils are mainly observed in the district- Sandy loam soil.


Crop
Pearl millet, castor, groundnut, Barley, Wheat, Amaranth, Quinoa, Mustard
Sustainability Efforts
Economic
| Women's Empowerment through Entrepreneurial Training Programs |
234 |
|
| Empowering Young Women: Career Counseling for Future Success |
454 |
|
| Craftsmanship Unleashed: Skill Development in Artisanal Handicrafts |
245 |
|
Social
| Nourishing the Future: Workshop on Child Nutrition and Well-being |
1200 |
|
| Guiding the Leaders of Tomorrow: Mentoring Programs for Students |
850 |
|
Environmental
| Cultivating the Earth: Advanced Training in Soil Regeneration |
355 |
|
| Towards a Plastic-Free Future: Comprehensive Reduce and Reuse Initiatives |
1233 |
|
| Preserving Our Lifeline: Campaigns for Water Conservation and Stewardship |
211 |
|
| Agriculture in Harmony with Nature: Organic Farming workshops |
986 |
|
| Clean Village, Healthy Village: Promoting Cleanliness and Sanitation at the Grassroots Level |
653 |
|
Impact
Impact of our Farmers
The impact of our farmers is significant in enhancing soil fertility through various methods such as crop rotation, cover cropping, reduced tillage, and application of compost. These practices reduce fuel-intensive tillage, resulting in carbon sequestration, decreasing greenhouse gases, and reversing climate change. In addition, they can improve soil structure and reduce the possibility of soil erosion.

Difference our People are Making
The difference our organization is making is by converting land from conventional management to organic management, managing the entire surrounding system for biodiversity and sustainability, and using alternative sources of nutrients such as crop rotation, residue management, and organic manures. We provide complete biological inputs to our crops, and our teams supervise and manage weed and pest control through better management practices, physical and cultural means.
Contribution by our Customers
Our customers’ contribution is vital in promoting food safety and environmental issues. The concern for their health, the environment, and worldwide crises has increased exponentially. Organic agriculture has become the only option for many consumers. Simply by consuming organic produce, they are contributing to the overall health of the planet and making an impact towards sustainability.