[layerslider id=”25″]
[layerslider id=”27″]
Let us tell you about the Chhatarpur project of Nature Bio Foods which is located on the far north-east border of Madhya Pradesh. It is 133 km from Jhansi in Uttar Pradesh and 233 km from Gwalior in Madhya Pradesh. 90% area of Chhatarpur Project falls in the state of Madhya Pradesh, India.
Chhatarpur is a major junction and happens to be a trade centre of agricultural products and fabrics. The region of Chhatarpur and nearby cities is a fertile plain due the woody elevation and rivers that surround them. This region is ideal for growing crops like rice, sorghum, wheat, barley, and legumes.
TRACEABILITY CODE: NBFPOR2014NO04CHI
Learn More About the Project

Location of the Project
Balrampur town located on the bank of Rapti river is district head quarter. Balrampur is known for its temple Devipatan a shakipeeth
Coordinates – Balrampur is located at 27.43°N 82.18°E.
Organic Certification

Bio Suisse is the Swiss organic market’s private label and the owner of the registered trademark Bud. Its standards are private law guidelines and exceed the minimum legal requirements in essential respects (EU-Eco-Regulation 834/2007 or equivalent).

Leo, quam commodo libero nulla mi. Gravida cursus in eget adipiscing amet risus odio. Orci adipiscing et, ultricies non enim. Pharetra, ornare est netus morbi integer nec nunc. Molestie viverra leo arcu fusce magna porta neque, mi. Sed eu rutrum augue porttitor pulvinar morbi fermentum semper. Purus etiam id non tincidunt nulla amet. Lobortis fusce mauris, elit etiam adipiscing pellentesque. Orci neque, quis sit nulla pretium hac laoreet nec urna.

Naturland promotes organic production and social recognition of organic agriculture worldwide. Their work enables them to contribute to protecting the environment and its resources, ensuring food security, and improving people’s living conditions. Naturland certification is attainable even for low-acreage farmers, they also work with producer associations that incorporate numerous individual producers. In this case, a producer association or ‘cooperative’ counts as one Naturland member.

Organic products are grown under a system of agriculture without the use of chemical fertilizers and pesticides with an environmentally and socially responsible approach. This is a method of farming that works at grass root level preserving the reproductive and regenerative capacity of the soil, good plant nutrition, and sound soil management, produces nutritious food rich in vitality and has resistance to diseases.
India is bestowed with a lot of potential to produce all varieties of organic products due to its various agro-climatic conditions.

The KRAV label has grown out of active interest to protect, nature, people, animals, and the future. Their goal is to contribute to sustainable and confidence-inspiring production of high-quality food in the long-term. Since 1985 KRAV has pursued the development of organic and sustainable food production, and thousands of actors in the food production chain have come together to support our goal. We are now Sweden’s most well-known environmental food label – 98% of all consumers are familiar with the KRAV label.

Biodynamic farming is a regenerative and holistic approach to agriculture, gardening, and food production and processing. It has higher standards than organic agriculture because it looks at the bigger picture and tries to put back more than it extracts.
Setting very high standards for organic farming since 1924. Developing from lectures given by scientist and philosopher, Rudolf Steiner, the pioneers in biodynamic farming has been developing this modern and future-oriented cultivation method ever since.
Social Certification

Fairtrade’s approach enables farmers and workers to have more control over their lives and decide how to invest in their future.
As a leader in the global movement to make trade fair, Fairtrade supports and challenges businesses and governments and connects farmers and workers with the people who buy their products.
Small-scale farmers and workers are among the most marginalized by the global trade system. At Fairtrade, they are at the heart of everything we do. Unique among certification schemes, producers have an equal say in how Fairtrade is run and are included in all our decision-making.
Everything you need to know about Balrampur
Balrampur town located on the bank of Rapti river is district head quarter. Balrampur is known for its temple Devipatan a shakipeeth.
In 2011, Balrampur had population of 2,148,665 of which male and female were 1,114,721 and 1,033,944 respectively. In 2001 census, Balrampur had a population of 1,682,350 of which males were 887,939 and remaining 794,411 were females. Balrampur District population constituted 1.08 percent of total Maharashtra population. Balrampur is located at 27.43°N 82.18°E. It has an average elevation of 105 metres (344 ft). The area of the district is 336917 Ha. In which the agriculture irrigated area is 221432 Ha. In the north of the district is situated the Shivalics ranges of the Himalyas which is called Tarai Region.
Agricultural Characteristics
Soil Profile

The soils of the project area consist broadly of “Matiyar” or clay, “Dumat” or loam. The hard clay soil or Matiyar is ideal for rice cultivation and very fertile. The Dumat or loam is also fertile soil, ideal for cultivation of various types of crops. This is the reason for high crop yields in the project area.

Soil Type 1

Soil Type 2

Soil Type 3
Climate Condition
Balrampur district comes under north eastern Plain zone which has a relatively sub tropical climate with high variation between summer and winter temperature. The temperature of the district varies from 5 0C during winter to 430C during summer. The maximum rainfall occurs in last week of July and first week of August. Hot waves flows in the month of May and cold waves during January the average rainfall of the district was 1100 mm. The forest cover in the district is 18.15% of the total geographical area which is dominated by Northern tropical mixed types of forest. Wide variation is soil, topography, climate and habitat made this district different from others which is lead variability in flora and fauna. It also bestowed with wide range of biodiversity and is rich in horticulture heritage and genetic wealth.
Temp.
Minimum

5°C
(Dec-Jan)
Maximum

45°C
(May-June)
Humidity
Minimum

5°C
(Dec-Jan)
Maximum

45°C
(May-June)
Rainfall
When compared with winter, the summers have much more rainfall.
South West
Mansoon
990 mm
(June-Sep)
North West
Mansoon
95 mm
(Oct-Jan)
Summer
Rains
15 mm
(Mar-May)
Seasons
There are mainly three seasons.

Summer
(Mar-June)

Rainy
(July-Sep)

Winter
(Oct-Feb)
Farm Water Availability
Most of the agriculture depend on the rain water , very few farmers has access to the canal irrigation water comes from Chitourgarh and Kohargaddy dam .Some farmers have access of tube well water also which are either private or government run tube well.
Nature of Farmers
Farmer of the district is very simple and hard working. Most of the population of district comes from farming backgrounds. Farmers are hardworking and following simple living.


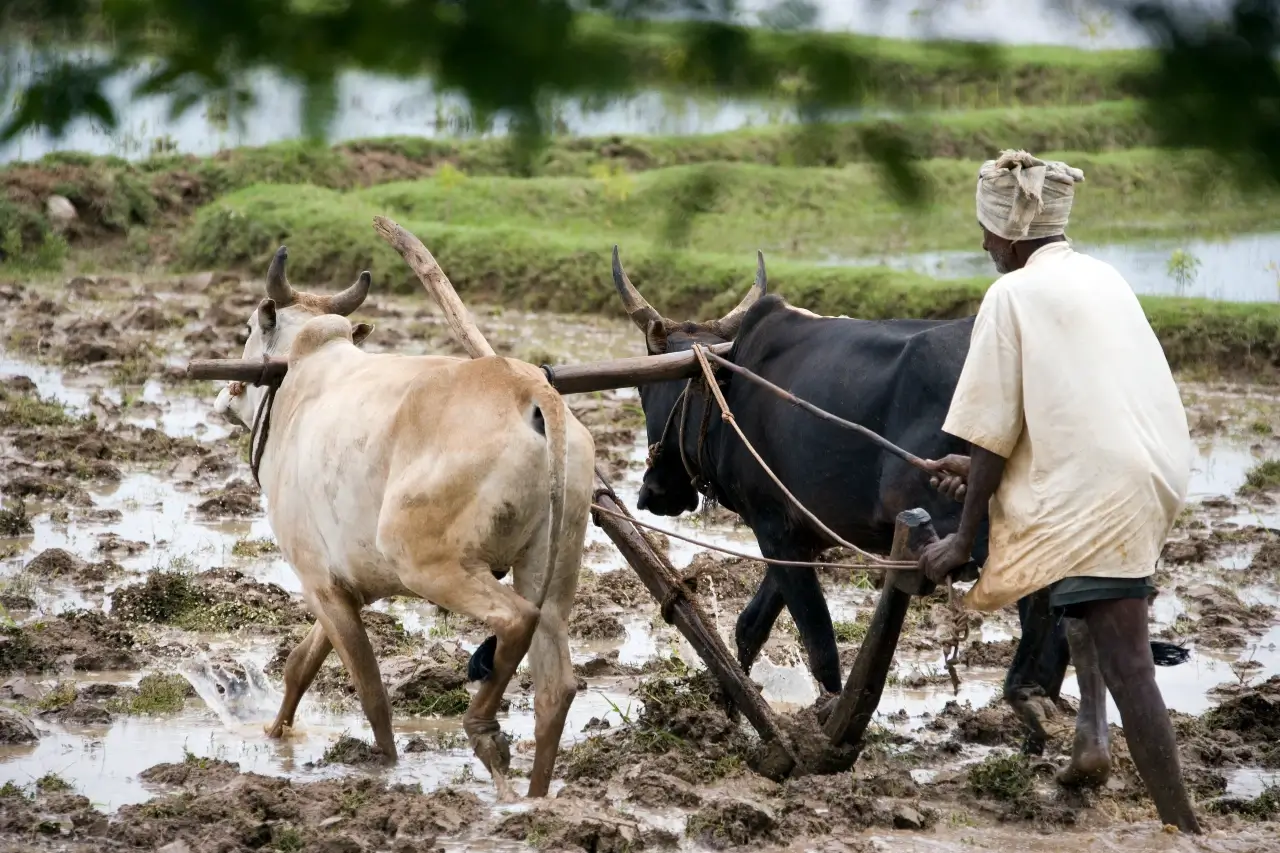
Growing Conditions
Rice-Wheat cropping system is most predominant .The average rice yields in this region are between 2600–2900 kg/ha and that of wheat between 2800–2950 kg/ha. Rice, maize, pigeon pea, moong bean crops are common in Kharif season. In post-rainy (Rabi) season wheat, lentil, mustered, pigean pea, and sesame and at some places groundnut is grown on residual soil moisture with one or two supplemental irrigation. The important cash crops of the region are sugarcane, the region has good climate. Predominantly there are three seasons—hot summer (April–June), hot and humid rainy season (July–October) and cool dry winter (November–March). The growing period ranges from 180–210 days in a year. Two crops are common but with irrigation, third crop can also be taken during summer. The rainfall in the region is good, ranging between 1,050–1,300 mm.
Crop Details
In Kharif season farmers grow basmati rice, Kala namak and hybrid variety of rice with maize and green pea while in Rabi season main cultivated crop is Wheat ,Pulses ,Flaxseed ,lentil along with coriander etc.
Rabi
- Wheat
- Mustured
- Lentil
- Flexseed
- Coriander

Kharif
- Non-Basmati
- Kala Namak paddy
- Basmati paddy
- Peagon pea
- Maize

Statistics
NBF Supply Chain
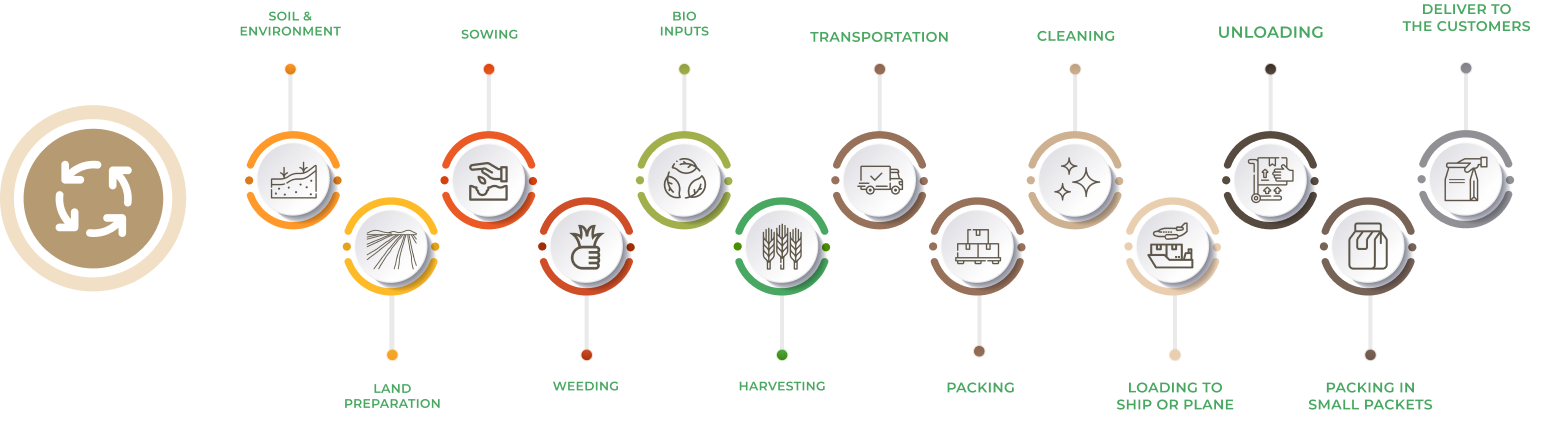
NBF Supply Chain
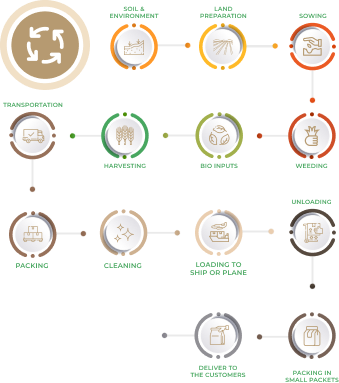
Process at a Glance

Clipping The Tip Of A Paddy Seeding
Yellow stem borer is a serious pest of rice, and its incidence is noticed in the nursery, planting to mid tillering, and panicle initiation stages. Heavy infestation results in 40-60 percent yield loss. Symptoms of damage include the presence of brown-colored egg masses near leaf tips in the nursery and early transplanted plants.
One of the control measures is to clip off the tip of the seedlings before transplanting and collect and destroy stem borer egg masses present on the transplanted young rice plants.
Team NBFL conducted 100+ field demonstrations of clipping the paddy seedlings before transplanting and collecting and destroying stem borer eggs.


Benefits Of Line Sowing Of Paddy
A scientific study revealed that the average increase in paddy yield was about 20 % under the line sowing method over the broadcast method of paddy planting. The per hectare net return was more under-line sowing as compared to the broadcasted method of sowing.
Also, line sowing is more effective due to easy intercultural operations like weeding, spraying, etc., and uniform plant stand.
Team NBF demonstrated this technology at 100 farmers’ fields.



Technology Demonstration & Training
Pheromone Traps for insect management
Waste Decomposer for crop residue decomposing & quality compost making
Vermi Compost units
Botanical Pesticides
Contamination control in produce
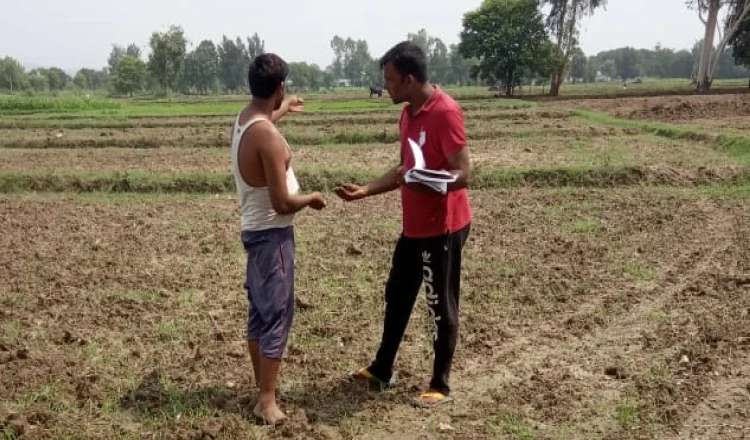



Demonstration Of Pheromone Trap
Pheromone traps are often used to catch certain species of insects and in these traps, a pheromone attractant is used to lure insects. Once attracted, a catching bucket captures the insect.
Pheromones are sex attractants that attract only males of various species of insects. These types of traps are not used to control insects but instead are used to detect the presence of pests, for monitoring, or to determine the first appearance of a pest in an area.
To manage the yellow stem borer of the paddy team NBFL demonstrated this trap at farmer’s fields.


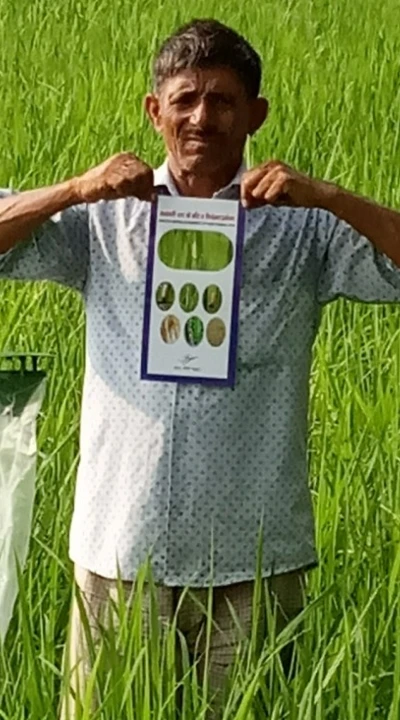
Weed Suppression
Green manure crops grow quickly and their very leafy growth smothers weeds. It is like a living mulch as it suppresses weeds and retains moisture in the soil. It is good practice to make sure the soil is weed-free first. That is why they are very important when areas are left fallow especially good in winter.
Demonstration Of Pheromone Trap
Improving Soil Structure
Green manures have deep penetrative roots that as they grow open up the soil. This is an advantage on heavy soils as allows drainage to occur more freely and organic matter to be left in the soil on lighter soils the particles of soil can bind together better so they can hold water better and leaves the organic matter in the soil.
Adding Nutrients
Leguminous green (Sesbania) manures absorb nitrogen from the air and fix it in root nodules on their roots so that when it is dug in it becomes available to the following crop. Specific soil bacteria are required to be present but they are usually present in healthy soil. Nitrogen is required by plants as it encourages healthy stem and leaf growth.


Technology Demonstration & Training
Pheromone Traps for insect management
Waste Decomposer for crop residue decomposing & quality compost making
Vermi Compost units
Botanical Pesticides
Contamination control in produce




Soil Sampling & testing
A soil test is important for several reasons: to optimize crop production, to protect the environment from contamination by runoff and leaching of excess fertilizers, to aid in the diagnosis of plant culture problems, to improve the nutritional balance of the growing media and to save money and conserve energy by applying only the amount of fertilizer needed. Pre-plant media analyses indicate potential nutrient deficiencies, pH imbalance, or excess soluble salts. This is particularly important for farmers who grow organic and use their own produced FYM.
In support of the department of agriculture Jammu, we have conducted soil analysis before the sowing of Rabi and Kharif crops every year and based on lab results recommend nutrient management practices to our growers.

How to Reach Chhatarpur?
Chattarpur is located in Madhya Pradesh, the heart of India. It is well connected to all the major zones of the nation.

By Train
The nearest Railway Station is Khajuraho Railway Station which is connected to the major cities of Madhya Pradesh.

By Road
Chhatarpur is 24 Kms from Nowgong, 54 Kms from Mahoba, 105 Kms from Banda, 133 Kms from Jhansi, 162 km from Sagar, 232 km from Shivpuri, 274 Kms from Vidisha, 342 Kms from Bhopal and is connected through Madhya Pradesh State Road Transport Corporation (MPSRTC) and some private travel services.
By Air
The nearest Domestic Airport is Khajuraho Airport, roughly 45 minutes drive from Chhatarpur. It is well connected to a spectrum of cities like Varanasi, Delhi and Agra. The nearest International Airport is Bhopal Airport, a roughly six-hour drive from Chhatarpur. Frequent Flights to various national and international destinations take off from here.

Places to Visit in Chhatarpur
Patan Devi Temple
The Khajuraho Group of Monuments is a group of Hindu temples and Jain temples in Chhatarpur district, Madhya Pradesh, India. They are a UNESCO World Heritage Site. The temples are famous for their nagara-style architectural symbolism and their erotic sculptures
Mahamongkol Chai Dhamma


Mountain
It has an average elevation of roughly 126 meters.


River
The beautiful Ghaghara river, a tributary of the Ganges, shapes the lands of Bahraich.


Soil
The soils of the district are very fertile. They consist of “Matiyar” also known as clay and “Dumat” also known as loam. The Matiyar is ideal for rice cultivation and the Dumat is ideal for the cultivation of various types of crops.


Crop
Kharif Season
Non-Basmati Paddy, Basmati paddy, Maize, Sesame
Rabi Season: Wheat, mustard, lentils etc.
Sustainability Efforts
Economic
Women Employment Generated
1200+ | ||
Average Farmer's Income Growth
20% | ||
Annual Employment Growth
9% | ||
Social
Schools Constructed
10+ | ||
Toilets Constructed
100+ | ||
Daily Meal Distributed
10,000+ | ||
Sanitization kits Distributed
10,000+ | ||
Blood Domination Camps
100+ | ||
Environmental
Trees Planted
99,978+ | ||
Sanitation Facilities Provided
100+ | ||
Solar Lamps Installed
1,000+ | ||
Gallon Rain Water Harvested
15,000+ | ||
KGs Plastic Waste Recycled
9.000+ | ||
Impact
Impact by our Farmers
Farmers use a variety of methods to improve soil fertility, including crop rotation, cover cropping, reduced tillage, and application of compost. By reducing fuel-intensive tillage, less soil organic matter is lost to the atmosphere. This has the added benefit of carbon sequestration, which reduces greenhouse gases and helps reverse climate change. Reducing tillage may also improve soil structure and reduce the potential for soil erosion.

Difference our People are Making
Multiple Processes starting Conversion of land from conventional management to organic management and Management of the entire surrounding system to ensure biodiversity and sustainability of the system. Also, Crop production with the use of alternative sources of nutrients such as crop rotation, residue management, organic manures, and providing complete biological inputs.
Management of weeds and pests by better management practices, physical and cultural means is supervised and managed by our teams thus being an integral contributor and impact to the cause.
Contribution by our Customers
Consumers’ attention to food safety issues and environmental issues has increased overwhelmingly in recent decades because of their increased concern about their own health, the environment’s health, and the crises and emergencies reported worldwide. Once the only option, organic agriculture has always been a production option followed by at least a few farmers all over the world, and consumers are directly contributing to the overall health of the planet and creating an impact by simply consuming.