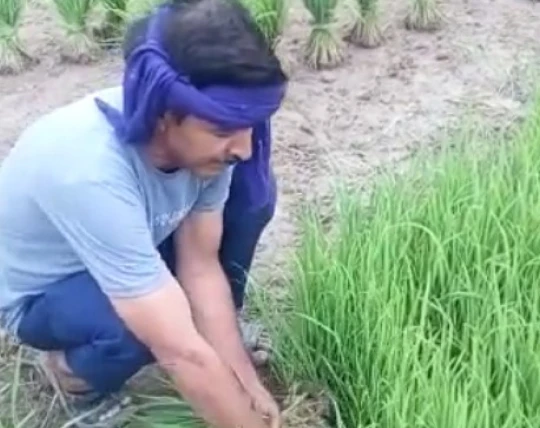
Khajuraho farmers cultivate a wide variety of organic and sustainably grown crops, such as Soyabean, Black Gram, Lentil, Barley, Wheat and more, which are then fine-graded and quality-tested before being distributed.

Grown in the organic plains of Central India
– Organic Farms of Khajuraho, Madhya Pradesh
Khajuraho farmers cultivate a wide variety of organic and sustainably grown crops, such as Soyabean, Black Gram, Lentil, Barley, Wheat and more, which are then fine-graded and quality-tested before being distributed.

Nature Bio Foods’ Khajuraho Project is is located on the far north-east border of Madhya Pradesh. It is 133 km from Jhansi in Uttar Pradesh and 233 km from Gwalior in Madhya Pradesh. 90% area of the Khajuraho Project falls in the state of Madhya Pradesh, India.
Khajuraho is a major junction and happens to be a trade center of agricultural products and fabrics. The region of Khajuraho and nearby cities is a fertile plain due to the woody elevation and rivers that surround them. This region is ideal for growing crops like rice, sorghum, wheat, barley, and legumes.
NBF’s Project Khajuraho

Location of the Project
The NBF’s Khajuraho project lies in the upper part of the Bundelkhand plateau known for its rugged terrain and rocky hills. The most notable aspects of the project are those which are crossed by the Panna Hill Range in the Southern parts. The region is also home to several rivers, including the Ken River and the Betwa River, which are important sources of water for irrigation and other uses.
Coordinates – Khajuraho project is located at 24.5500°N 79.3527°E.
Social Certification

Fairtrade Certified Khajuraho Project

NBF complies with Fairtrade’s approach to enable farmers and workers to have more control over their lives and decide how to invest in their future. Our Khajuraho project aligns with Fairtrade’s approach to empowering farmers and workers to have greater control over their lives and invest in their future. We fully support Fairtrade’s standards and associated norms, and we’re proud to integrate them into our business practices.
When you see the FAIRTRADE Mark on our products, you can trust that we’ve met internationally agreed-upon standards that have been independently verified. At NBF, we prioritize fairness and ethical practices in all aspects of our business, and our commitment to Fairtrade is an essential part of that.
We believe in empowering farmers and workers at NBF, which is why they have a strong voice at every level of trade. From managing their farms to contributing to our discussion forums, we’re dedicated to providing an equal platform for everyone. Our adherence to Fairtrade’s principles is not just about compliance; it’s a core value that guides our business.
Fairtrade is more than just a certification at NBF; it’s a way of doing business that puts people first. We’ve followed Fairtrade practices and implemented measures that provide better prices and working conditions for farmers and workers. By doing so, we’re helping to create a fairer deal for those who work hard to produce our products.
Welfare Activities under Fairtrade by Nature Bio Foods in NBF Khajuraho Project
Nature Bio Foods’ NBF Khajuraho Project has been instrumental in uplifting the community’s well-being and fostering sustainable development in the region. Recognizing its outstanding efforts, the project was honored with the prestigious Bundelkhand Ratan Samman, celebrating its commitment to the principles of Fairtrade and social responsibility.

Health: Community Health Centre (CHC)
Nature Bio Foods took on the responsibility of renovating and upgrading the Community Health Centre in Taparian Village. Through this initiative, the CHC was equipped with modern facilities, ensuring that the center operates smoothly and efficiently. With continuous support from Nature Bio Foods, the CHC now accommodates an average of 40 patients per day, catering to the healthcare needs of the community.

Water Project – Check Dam & Ponds Construction for Water Conservation
Water conservation has been a paramount concern in the drought-prone region. To combat water wastage and promote sustainable water management, Nature Bio Foods undertook the construction of three check dams and one pond. These structures have collectively saved millions of liters of water, providing irrigation support for agricultural lands and bolstering the region’s water resources.

Clean Drinking Water – Community Water Filters & Household Water Filters
Addressing the challenge of clean drinking water, Nature Bio Foods distributed 700 household water filters, benefitting around 3500 individuals. Additionally, 14 community RO water filters were installed, providing clean and safe drinking water to approximately 6600 beneficiaries.

Water Project – Water Wheels
In response to the struggles faced by villagers during dry spells, Nature Bio Foods distributed 200 water wheels in 2022-23. These innovative devices eased the burden of carrying water over long distances, significantly improving the lives of families in the region.

Livelihood Support – Goat Rearing Project
Nature Bio Foods initiated the Goat Rearing Project, distributing Sirohi breed goats to 199 poor and needy families in the Khajuraho project location. This project has made a significant impact, with a total of 289 goats benefiting these families. The goats not only provide a source of livelihood but also contribute to the community’s nutrition, producing over 40,000 liters of milk annually. With an average yearly income ranging from INR 12,000 to INR 15,000, the Goat Rearing Project has empowered families to achieve financial stability.

Agri Support – Usages of Agri-Implements (Machineries)
Through the operation of an Agriculture Service Center by a Self-Help Group, Nature Bio Foods made available various agricultural machinery on subsidized rates. Beneficiaries have access to essential equipment such as Multi-crop Threshers, Seed Drills, Cultivators, Summer Ploughs, and Spray Pumps, facilitating efficient crop cultivation and harvesting. The distribution of high-quality seeds, in collaboration with local government authorities, further enhances agricultural practices in the selected villages, promoting sustainable farming methods.

Solar Street Lights
With a strong commitment to sustainable energy, the NBF Khajuraho Project successfully installed 159 solar street lights in FY 2022-23, adding to the existing total of 323 solar street lights. Ensuring 100% operational efficiency, these solar lights illuminate the villages, enhancing safety and contributing to reduced carbon emissions.

Education Project – School Adoption Program
Nature Bio Foods’ dedication to education is evident through its School Adoption Program. By adopting 15 schools, the project has positively impacted 2375 students’ lives, providing them with essential support and resources. As part of this initiative, 10 digital classrooms have been established, promoting modern and technology-driven education.

Infrastructure Development – Roads, Drainage & Community Centres
Nature Bio Foods extended its efforts towards infrastructure development, covering six villages under the Roads and Drainage project. This crucial undertaking ensures improved connectivity and accessibility for the communities. Additionally, three community centers have been established, serving as vital hubs for social gatherings and community activities.
Case Study for NBF Khajuraho Project
NBF Khajuraho Project stands as a shining example of Fairtrade principles in action, with a strong focus on social welfare, environmental conservation, and community development. Through the relentless dedication and holistic approach of Nature Bio Foods, the project has successfully transformed the lives of countless individuals in the region, creating a positive ripple effect on both the present and future generations. The Bundelkhand Ratan Samman recognition further underscores the project’s profound impact, inspiring continued efforts towards sustainable and equitable development.
Organic Certification
Demeter Certified Khajuraho Project

BIODYNAMICS –
STARTING FROM THE GROUND UP
KEEPING UP
HIGH STANDARDS

Nature Bio Foods has implemented the Demeter biodynamic farming practices in its project in Khajuraho. The project has received Demeter International certification, which recognizes the highest standards of biodynamic agriculture.
NBF project in Khajuraho involves working closely with local farmers to promote biodynamic farming practices. Nature Bio Foods provides training and technical support to farmers, as well as access to organic and biodynamic seeds and other inputs, to help them transition to biodynamic farming. The Demeter International certification to NBF ensures our products are produced according to the highest standards of biodynamic agriculture. The implementation of Demeter biodynamic farming practices in the project in Khajuraho reflects Nature Bio Foods’ commitment to promoting sustainable agriculture and supporting local communities.



Khajuraho Project Certified By Naturland and BioSuisse Organic

Nature Bio Foods’ Khajuraho project proudly holds Naturland certification, strengthening the commitment to organic agriculture and fostering the prosperity of smallholder farmers. Naturland certification is attainable even for low-acreage farmers, and they work with producer associations that incorporate numerous individual producers. By working with Naturland, NBF is enabling smallholder farmers to adopt sustainable and organic farming practices while gaining access to premium markets for their produce. NBF’s partnership with Naturland not only benefits the environment but also supports the livelihoods of smallholder farmers. By promoting sustainable and organic agriculture, NBF is helping to increase the income and resilience of farmers from Khajuraho region, while also contributing to global efforts towards a more sustainable food system.

Nature Bio Foods’ Khajuraho project has successfully implemented the Bio Suisse organic certification in its project, ensuring that their products meet the highest standards of organic farming. The Bio Suisse certification is a globally recognized standard for organic farming, which requires farmers to follow strict guidelines for environmental sustainability, animal welfare, and social responsibility. The Khajuraho project has been certified by Bio Suisse, which is a testament to their commitment to sustainable agriculture and responsible farming practices. With this certification, consumers can be assured that Nature Bio Foods’ products are of the highest quality and are produced in an environmentally and socially responsible manner.
Everything you need to know about Khajuraho
Beholding the spectacular view of Raneh Falls to the Ken Gharial Sanctuary situated at the Sangam of Ken and Khudar Rivers, the territory of Khajuraho entails various picturesque tourist sites to discover! Moreover, the district shares several major borders such as the Panna from the east, Tikamgarh from the west, Damoh from the south, Sagar from the southwest, and lastly, Uttar Pradesh from the north.
The Khajuraho project lies in the upper part of the Bundelkhand plateau. The most prominent parts of the project are those which are transverse by the Panna Hill Range through the Southern parts. The range stands about 100 m from the surrounding and 300 m from the mean sea level. From here the plateau lowers down and covers into the alluvial plains in the north, particularly along with the Ken and Dhawan rivers. The lands of Bundelkhand are lying between south of Yamuna, east of Betwa, west of the temple of Vindhyavasini Devi, and north of the Narmada rivers. Thus, there are three physical divisions of the area namely:
(A) The Panna Range – The Panna Range is a branch of the Vindhyan Mountains. It traverses Sagar, Chhatarpur, and Panna Districts from the southwest to northeast, The highest peak in the district lies at 240 27` north by 790 45` east.
(B) The Central Plateau – The Central Plateau runs to the north as an offshoot of the Panna Range. It lies mainly on the Bundelkhand granites and forms the central sub-water divide.
(C) The Northern Plains – The Northern Plains lie between 152-300 m above mean sea level and cover nearly the whole Laundi district. It is covered by varying thicknesses of aluminum but it is a cut of ravines.
Agricultural Characteristics
Soil Profile

The soils in Bundelkhand are divided into four groups: Rakar, Parwa, Kabar, and Mar. These groups differ in their physical and chemical properties. The majority of the region’s soils are light black, which is ideal for high productivity agriculture. Some parts of the region also have black and red mixed soils. However, most soils in the area have a low water holding capacity. The soil profile can be categorized into three types: deep soils (30% of the area), medium deep soils (30% of the area), and shallow soils (40% of the area).

Deep Soil: Found in 30% of the area, deep soils in Bundelkhand offer good depth and are favorable for agricultural productivity. They provide ample room for root development and have relatively higher water-holding capacity.

Medium Deep Soil: Covering 30% of the region, medium deep soils have a moderate depth and water-holding capacity. They strike a balance between deep and shallow soils, offering satisfactory conditions for crop growth.
Shallow Soil: Constituting 40% of the area, shallow soils in Bundelkhand have limited depth and lower water-holding capacity. These soils require careful management and irrigation practices to support crop cultivation effectively.
Climate Condition
Khajuraho has a tropical climate with hot summers and mild winters. The monsoon season starts in June and lasts until September, with the heaviest rainfall in July and August. The best time to visit Khajuraho is from October to March when the weather is pleasant and suitable for sightseeing.
Temp.
Minimum

5°C
(Dec-Jan)
Maximum

43°C
(May-June)
Humidity
Minimum

25%
(Dec-Jan)
Maximum

85%
(May-June)
Rainfall
The average annual rainfall of the region is
1100 mm which distribution is as follow.
South West
Mansoon
990 mm
(June-Sep)
North West
Mansoon
95 mm
(Oct-Jan)
Summer
Rains
15 mm
(Mar-May)
Seasons
There are mainly three seasons.

Summer
(Mar-June)

Rainy
(July-Sep)

Winter
(Oct-Feb)
Farm Water Availability
In this region, 55% of the land is dependent on rainfall for agriculture, while only 45% has access to irrigation systems. The sources of farm water availability are open wells (77%), reservoirs (13%), canals (5%), bore wells (3%), and farm ponds (2%). Farmers in the region mostly use flood irrigation patterns, while lift and micro-irrigation systems are installed in a small area. The groundwater quality in the region is mildly alkaline.
Nature of Farmers
The farmers in Khajuraho are hardworking and dedicated individuals who have a deep connection to the land and its agricultural traditions. Agriculture is a primary source of livelihood for a significant portion of the population in Khajuraho, and many farmers have been practicing agriculture for generations. They possess a wealth of knowledge about crop cultivation, irrigation techniques, and traditional farming practices.
In the region, most farmers face literacy challenges, as they are unable to read and write. However, they have a great respect for people coming from outside their community. The farmers are also deeply attached to their old traditions and customs, but they are open to implementing new technology in farming. In fact, they are cooperative when it comes to adopting new techniques for better yields. The farmers are always eager to learn and get new inputs in the context of farming, which they believe will help them improve their agricultural practices.


Growing Conditions
The region boasts an abundance of natural forest wealth, which creates a suitable micro-climate for organic farming. As a result, natural components are readily available to the crops grown in the area. The farmers in the region use only traditional seeds, which helps to maintain international level quality standards by avoiding contamination from hybrid and GMO seeds.
Since most of the agriculture in the division is rain-fed, farmers adopt dry land agriculture practices, which create favorable conditions for the cultivation of pulses, oilseeds, and minor millets, resulting in high-quality produce.
Due to the low purchasing power of the farmers, the region has been left out of the grip of modern chemical agriculture. This has created favorable conditions for the further advancement of traditional farming practices, which can lead to sustainable agriculture in the long run.
Crop Details
The region’s fertile soil is ideal for the cultivation of crops such as Seasame, Barley , Quinoa , and Moong Bean. The abundant supply of water from rivers, lakes, and groundwater sources also supports the region’s thriving agricultural sector.
Kharif
- Soyabean
- Black Gram
- Seasame (White grain)
- Groundnut
- Bajra
- Moong Bean
- Seasame (Black grain)
- Pegionpea, Ginger

Rabi
- Chickpea
- Wheat
- Lentil
- Pea
- Mustard
- Barley
- Amaranth
- Flax
- Quinoa

Statistics
NBF Supply Chain
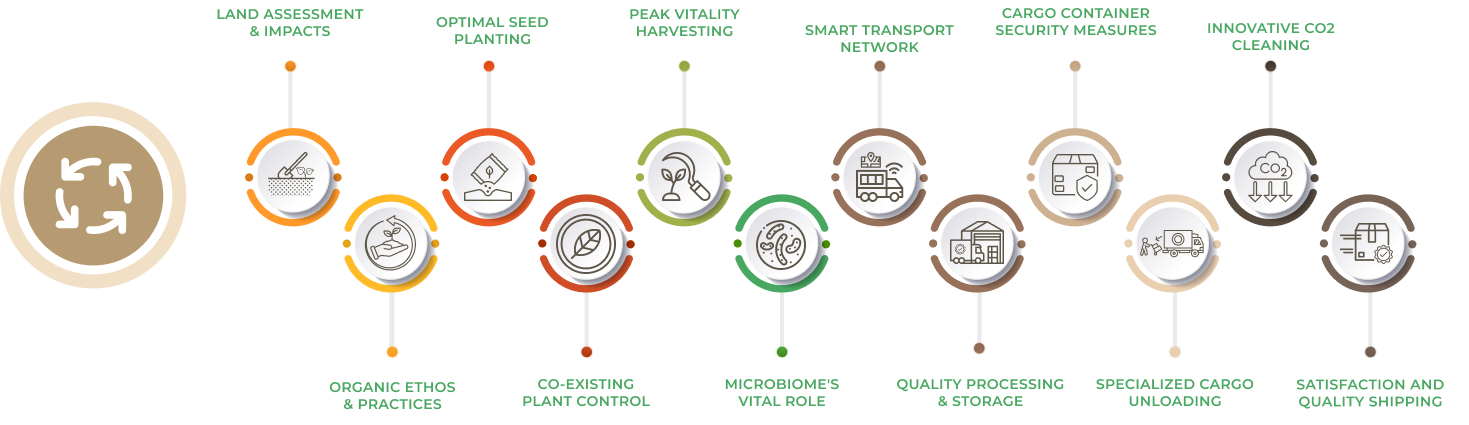
NBF Supply Chain
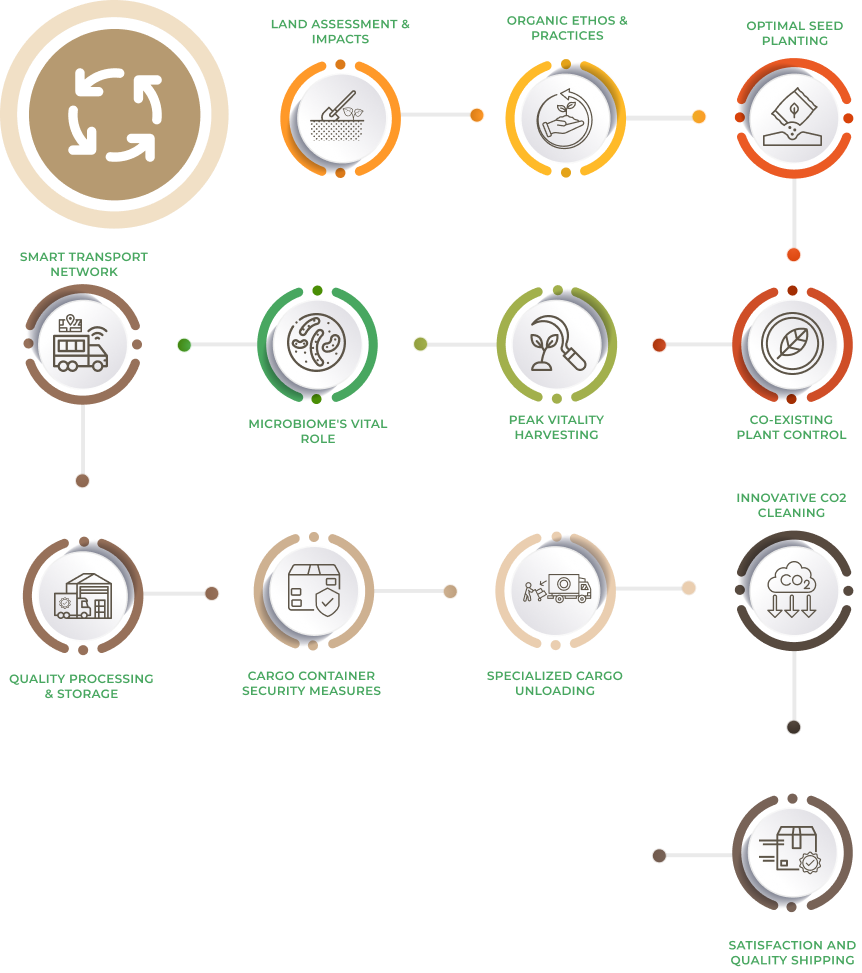
How to Reach Khajuraho, Madhya Pradesh?
Khajuraho, located in the Chhatarpur district of Madhya Pradesh, India, can be reached through various modes of transportation. There are several options to get around the city.

By Train
The Khajuraho Railway Station is connected to major cities like Delhi, Mumbai, and Varanasi, among others. Several express trains and superfast trains run on this route, making train travel a convenient option for reaching Khajuraho.

By Road
Khajuraho is well-connected by road with major cities in Madhya Pradesh and neighboring states. The city is located on National Highway 39, which connects it with cities like Jhansi, Satna, and Bhopal. State-run buses and private taxis are available for traveling to Khajuraho.
By Air
The Khajuraho Airport is well-connected with major cities like Delhi, Mumbai, and Varanasi. Regular flights are available from these cities to Khajuraho, making air travel a convenient option for reaching the city.

Places to Visit in Khajuraho, Madhya Pradesh
Khajuraho Temples
The Khajuraho Temples are a UNESCO World Heritage Site and one of the most popular tourist attractions in India. Built between 950 AD and 1050 AD by the Chandela dynasty, these temples are known for their stunning architecture and intricate stone carvings. The temples are divided into three groups, namely Western, Eastern, and Southern, and each group has its unique features. Some of the notable temples to visit include the Kandariya Mahadeva Temple, Lakshmana Temple, and Chitragupta Temple.
[/mvc_ihe]Panna National Park
Located approximately 25 km from Khajuraho, Panna National Park is a must-visit destination for wildlife enthusiasts. Spread over an area of 542 sq km, the park is home to a wide variety of flora and fauna, including tigers, leopards, chital, sambar, and wild boars. Visitors can take a jeep safari or an elephant safari to explore the park and spot these animals in their natural habitat. The park also has several waterfalls and viewpoints, making it a picturesque destination for nature lovers.
[/mvc_ihe]

Elevation
It has an average elevation of roughly 283 meters.


River
The Raneh Fall is a natural waterfall on the Ken River, located in Khajuraho in the Indian state of Madhya Pradesh.


Soil
The soil profile can be categorized into three types: deep soils (30% of the area), medium deep soils (30% of the area), and shallow soils (40% of the area).


Crop
Soyabean, Black Gram, Seasame (White grain), Groundnut, Bajra
Sustainability Efforts
Economic
| RO Purifiers: Water Filtration Systems for every Household |
700 |
|
| Advanced Water Purification System for Educational Institutions |
6 |
|
| Transforming Classrooms: Digitized Learning Spaces |
10 |
|
| Empowering Communities with Accessible Water Filtration Solutions |
8 |
|
| Illuminating Streets with Environment-Friendly Solar Lighting |
100 |
|
| Women's Empowerment through Entrepreneurial Training Programs |
564 |
|
| Empowering Young Women: Career Counseling for Future Success |
243 |
|
| Craftsmanship Unleashed: Skill Development in Artisanal Handicrafts |
435 |
|
Social
| Fostering Educational Partnerships: Village School Adoption Program |
14 |
|
| Students Holistic Development |
2489 |
|
| Championing Menstrual Hygiene: Centers for Women's Well-being |
1 |
|
| Enhancing Women's Health: Distribution of Menstrual Hygiene Products |
52114 |
|
| Empowering Women through Education: Menstrual Hygiene Training Initiatives |
6331 |
|
| Nourishing the Future: Workshop on Child Nutrition and Well-being |
1050 |
|
| Guiding the Leaders of Tomorrow: Mentoring Programs for Students |
750 |
|
Environmental
| Revitalizing Water Bodies: Pond Construction and Restoration Initiatives |
7 |
|
| Greening the Earth: Extensive Tree Plantation Drives |
40000 |
|
| Cultivating the Earth: Advanced Training in Soil Regeneration |
546 |
|
| Towards a Plastic-Free Future: Comprehensive Reduce and Reuse Initiatives |
895 |
|
| Preserving Our Lifeline: Campaigns for Water Conservation and Stewardship |
1432 |
|
| Agriculture in Harmony with Nature: Organic Farming workshops |
123 |
|
| Clean Village, Healthy Village: Promoting Cleanliness and Sanitation at the Grassroots Level |
986 |
|